Integrating with Confluent Cloud
DataHub provides the ability to easily leverage Confluent Cloud as your Kafka provider. To do so, you'll need to configure DataHub to talk to a broker and schema registry hosted by Confluent.
Doing this is a matter of configuring the Kafka Producer and Consumers used by DataHub correctly. There are 2 places where Kafka configuration should be provided: the metadata service (GMS) and the frontend server (datahub-frontend). Follow the steps below to configure these components for your deployment.
Step 1: Create topics in Confluent Control Center
First, you'll need to create following new topics in the Confluent Control Center. By default they have the following names:
- MetadataChangeProposal_v1
- FailedMetadataChangeProposal_v1
- MetadataChangeLog_Versioned_v1
- MetadataChangeLog_Timeseries_v1
- DataHubUsageEvent_v1: User behavior tracking event for UI
- (Deprecated) MetadataChangeEvent_v4: Metadata change proposal messages
- (Deprecated) MetadataAuditEvent_v4: Metadata change log messages
- (Deprecated) FailedMetadataChangeEvent_v4: Failed to process #1 event
- MetadataGraphEvent_v4:
- MetadataGraphEvent_v4:
- PlatformEvent_v1
- DataHubUpgradeHistory_v1: Notifies the end of DataHub Upgrade job so dependants can act accordingly (eg, startup). Note this topic requires special configuration: Infinite retention. Also, 1 partition is enough for the occasional traffic.
The first five are the most important, and are explained in more depth in MCP/MCL. The final topics are those which are deprecated but still used under certain circumstances. It is likely that in the future they will be completely decommissioned.
To create the topics, navigate to your Cluster and click "Create Topic". Feel free to tweak the default topic configurations to match your preferences.
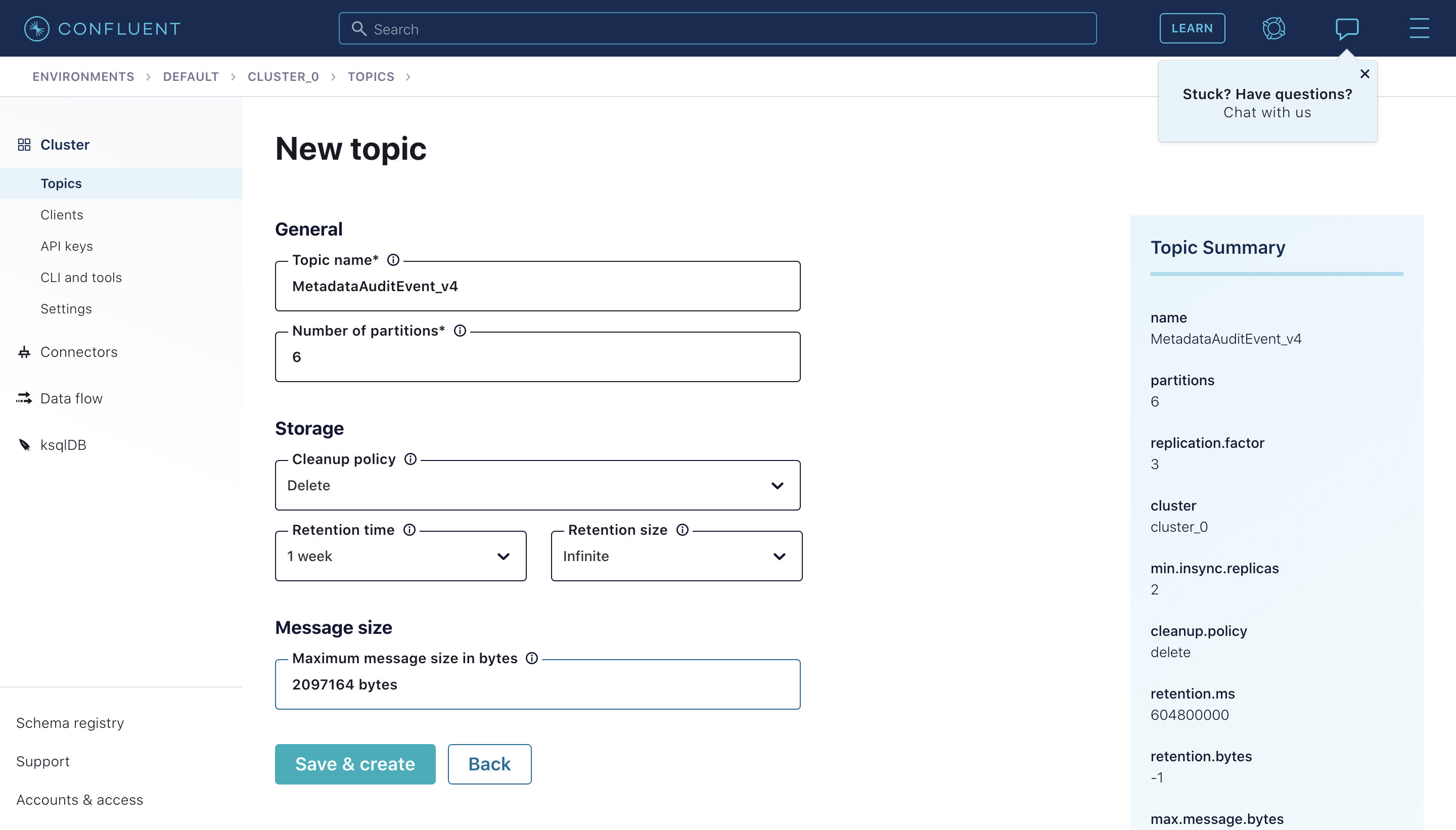
Step 2: Configure DataHub Container to use Confluent Cloud Topics
Docker Compose
If you are deploying DataHub via docker compose, enabling connection to Confluent is a matter of a) creating topics in the Confluent Control Center and b) changing the default container environment variables.
First, configure GMS to connect to Confluent Cloud by changing docker/gms/env/docker.env:
KAFKA_BOOTSTRAP_SERVER=pkc-g4ml2.eu-west-2.aws.confluent.cloud:9092
KAFKA_SCHEMAREGISTRY_URL=https://plrm-qwlpp.us-east-2.aws.confluent.cloud
# Confluent Cloud Configs
SPRING_KAFKA_PROPERTIES_SECURITY_PROTOCOL=SASL_SSL
SPRING_KAFKA_PROPERTIES_SASL_JAAS_CONFIG=org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required username='XFA45EL1QFUQP4PA' password='ltyf96EvR1YYutsjLB3ZYfrk+yfCXD8sQHCE3EMp57A2jNs4RR7J1bU9k6lM6rU';
SPRING_KAFKA_PROPERTIES_SASL_MECHANISM=PLAIN
SPRING_KAFKA_PROPERTIES_CLIENT_DNS_LOOKUP=use_all_dns_ips
SPRING_KAFKA_PROPERTIES_BASIC_AUTH_CREDENTIALS_SOURCE=USER_INFO
SPRING_KAFKA_PROPERTIES_BASIC_AUTH_USER_INFO=P2ETAN5QR2LCWL14:RTjqw7AfETDl0RZo/7R0123LhPYs2TGjFKmvMWUFnlJ3uKubFbB1Sfs7aOjjNi1m23
Next, configure datahub-frontend to connect to Confluent Cloud by changing docker/datahub-frontend/env/docker.env:
KAFKA_BOOTSTRAP_SERVER=pkc-g4ml2.eu-west-2.aws.confluent.cloud:9092
# Confluent Cloud Configs
KAFKA_PROPERTIES_SECURITY_PROTOCOL=SASL_SSL
KAFKA_PROPERTIES_SASL_JAAS_CONFIG=org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required username='XFA45EL1QFUQP4PA' password='ltyf96EvR1YYutsjLB3ZYfrk+yfCXD8sQHCE3EMp57A2jNs4RR7J1bU9k6lM6rU';
KAFKA_PROPERTIES_SASL_MECHANISM=PLAIN
KAFKA_PROPERTIES_CLIENT_DNS_LOOKUP=use_all_dns_ips
KAFKA_PROPERTIES_BASIC_AUTH_CREDENTIALS_SOURCE=USER_INFO
KAFKA_PROPERTIES_BASIC_AUTH_USER_INFO=P2ETAN5QR2LCWL14:RTjqw7AfETDl0RZo/7R0123LhPYs2TGjFKmvMWUFnlJ3uKubFbB1Sfs7aOjjNi1m23
Note that this step is only required if DATAHUB_ANALYTICS_ENABLED environment variable is not explicitly set to false for the datahub-frontend
container.
If you're deploying with Docker Compose, you do not need to deploy the Zookeeper, Kafka Broker, or Schema Registry containers that ship by default.
DataHub Actions
Configuring Confluent Cloud for DataHub Actions requires some additional edits to your executor.yaml. Under the Kafka
source connection config you will need to add the Python style client connection information:
connection:
bootstrap: ${KAFKA_BOOTSTRAP_SERVER:-localhost:9092}
schema_registry_url: ${SCHEMA_REGISTRY_URL:-http://localhost:8081}
consumer_config:
security.protocol: ${KAFKA_PROPERTIES_SECURITY_PROTOCOL:-PLAINTEXT}
sasl.mechanism: ${KAFKA_PROPERTIES_SASL_MECHANISM:-PLAIN}
sasl.username: ${KAFKA_PROPERTIES_SASL_USERNAME}
sasl.password: ${KAFKA_PROPERTIES_SASL_PASSWORD}
schema_registry_config:
basic.auth.user.info: ${KAFKA_PROPERTIES_BASIC_AUTH_USER_INFO}
Specifically sasl.username and sasl.password are the differences from the base executor.yaml example file.
Additionally, you will need to set up environment variables for KAFKA_PROPERTIES_SASL_USERNAME and KAFKA_PROPERTIES_SASL_PASSWORD
which will use the same username and API Key you generated for the JAAS config.
See Overwriting a System Action Config for detailed reflection procedures.
Next, configure datahub-actions to connect to Confluent Cloud by changing docker/datahub-actions/env/docker.env:
KAFKA_BOOTSTRAP_SERVER=pkc-g4ml2.eu-west-2.aws.confluent.cloud:9092
SCHEMA_REGISTRY_URL=https://plrm-qwlpp.us-east-2.aws.confluent.cloud
# Confluent Cloud Configs
KAFKA_PROPERTIES_SECURITY_PROTOCOL=SASL_SSL
KAFKA_PROPERTIES_SASL_USERNAME=XFA45EL1QFUQP4PA
KAFKA_PROPERTIES_SASL_PASSWORD=ltyf96EvR1YYutsjLB3ZYfrk+yfCXD8sQHCE3EMp57A2jNs4RR7J1bU9k6lM6rU
KAFKA_PROPERTIES_SASL_MECHANISM=PLAIN
KAFKA_PROPERTIES_CLIENT_DNS_LOOKUP=use_all_dns_ips
KAFKA_PROPERTIES_BASIC_AUTH_CREDENTIALS_SOURCE=USER_INFO
KAFKA_PROPERTIES_BASIC_AUTH_USER_INFO=P2ETAN5QR2LCWL14:RTjqw7AfETDl0RZo/7R0123LhPYs2TGjFKmvMWUFnlJ3uKubFbB1Sfs7aOjjNi1m23
Helm
If you're deploying on K8s using Helm, you can simply change the datahub-helm values.yml to point to Confluent Cloud and disable some default containers:
First, disable the cp-schema-registry service:
cp-schema-registry:
enabled: false
Next, disable the kafkaSetupJob service:
kafkaSetupJob:
enabled: false
Then, update the kafka configurations to point to your Confluent Cloud broker and schema registry instance, along with the topics you've created in Step 1:
kafka:
bootstrap:
server: pkc-g4ml2.eu-west-2.aws.confluent.cloud:9092
schemaregistry:
url: https://plrm-qwlpp.us-east-2.aws.confluent.cloud
Next, you'll want to create 2 new Kubernetes secrets, one for the JaaS configuration which contains the username and password for Confluent, and another for the user info used for connecting to the schema registry. You'll find the values for each within the Confluent Control Center. Specifically, select "Clients" -> "Configure new Java Client". You should see a page like the following:
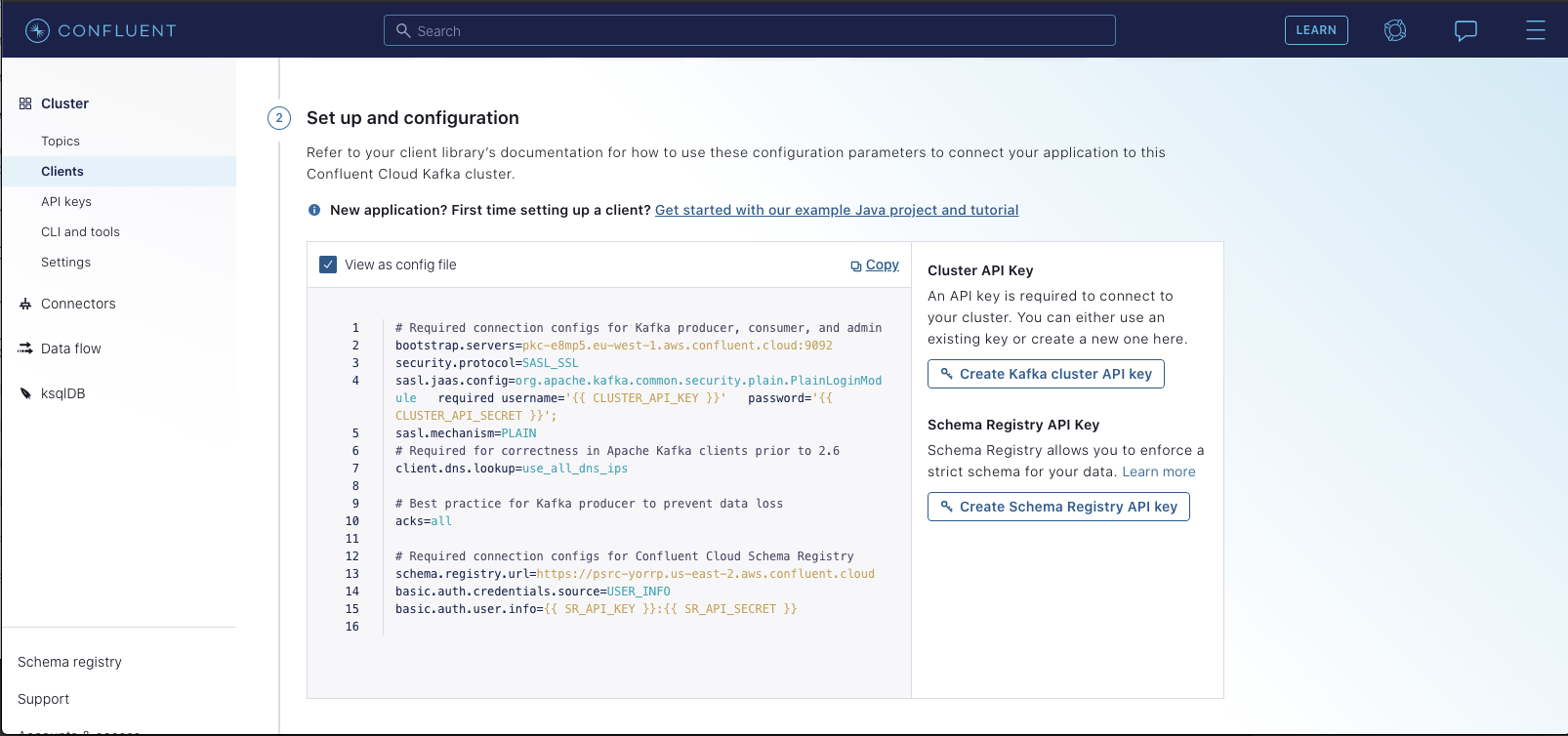
You'll want to generate both a Kafka Cluster API Key & a Schema Registry key. Once you do so,you should see the config automatically populate with your new secrets:
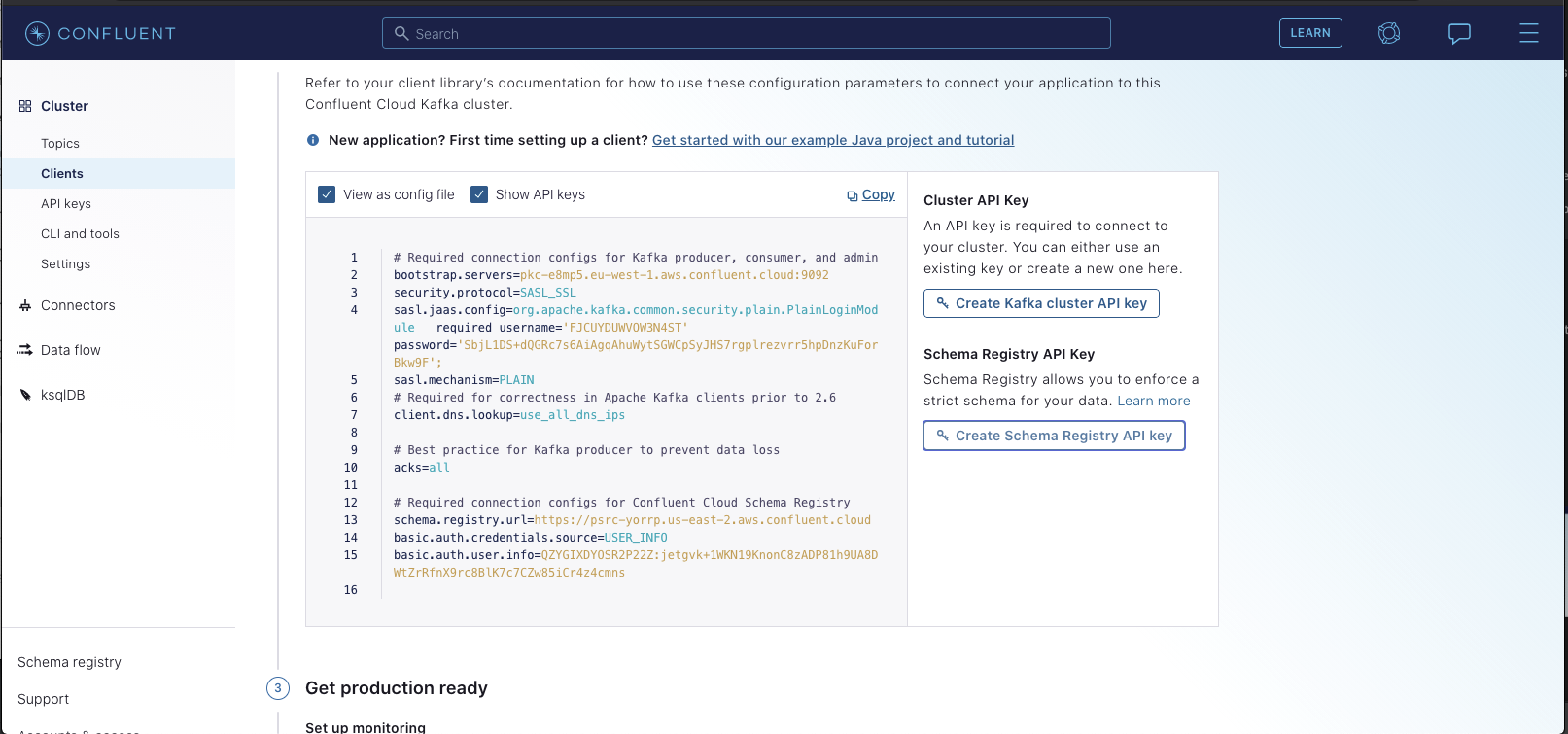
You'll need to copy the values of sasl.jaas.config and basic.auth.user.info
for the next step.
The next step is to create K8s secrets containing the config values you've just generated. Specifically, you can run the following commands:
kubectl create secret generic confluent-secrets --from-literal=sasl_jaas_config="<your-sasl.jaas.config>"
kubectl create secret generic confluent-secrets --from-literal=basic_auth_user_info="<your-basic.auth.user.info>"
With your config values substituted as appropriate. For example, in our case we'd run:
kubectl create secret generic confluent-secrets --from-literal=sasl_jaas_config="org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required username='XFA45EL1QFUQP4PA' password='ltyf96EvR1YYutsjLB3ZYfrk+yfCXD8sQHCE3EMp57A2jNs4RR7J1bU9k6lM6rU';"
kubectl create secret generic confluent-secrets --from-literal=basic_auth_user_info="P2ETAN5QR2LCWL14:RTjqw7AfETDl0RZo/7R0123LhPYs2TGjFKmvMWUFnlJ3uKubFbB1Sfs7aOjjNi1m23"
Finally, we'll configure our containers to pick up the Confluent Kafka Configs by changing two config blocks in our values.yaml file. You
should see these blocks commented at the bottom of the template. You'll want to uncomment them and set them to the following values:
credentialsAndCertsSecrets:
name: confluent-secrets
secureEnv:
sasl.jaas.config: sasl_jaas_config
basic.auth.user.info: basic_auth_user_info
springKafkaConfigurationOverrides:
security.protocol: SASL_SSL
sasl.mechanism: PLAIN
client.dns.lookup: use_all_dns_ips
basic.auth.credentials.source: USER_INFO
Then simply apply the updated values.yaml to your K8s cluster via kubectl apply.
DataHub Actions
Configuring Confluent Cloud for DataHub Actions requires some additional edits to your executor.yaml. Under the Kafka
source connection config you will need to add the Python style client connection information:
connection:
bootstrap: ${KAFKA_BOOTSTRAP_SERVER:-localhost:9092}
schema_registry_url: ${SCHEMA_REGISTRY_URL:-http://localhost:8081}
consumer_config:
security.protocol: ${KAFKA_PROPERTIES_SECURITY_PROTOCOL:-PLAINTEXT}
sasl.mechanism: ${KAFKA_PROPERTIES_SASL_MECHANISM:-PLAIN}
sasl.username: ${KAFKA_PROPERTIES_SASL_USERNAME}
sasl.password: ${KAFKA_PROPERTIES_SASL_PASSWORD}
schema_registry_config:
basic.auth.user.info: ${KAFKA_PROPERTIES_BASIC_AUTH_USER_INFO}
Specifically sasl.username and sasl.password are the differences from the base executor.yaml example file.
Additionally, you will need to set up secrets for KAFKA_PROPERTIES_SASL_USERNAME and KAFKA_PROPERTIES_SASL_PASSWORD
which will use the same username and API Key you generated for the JAAS config.
See Overwriting a System Action Config for detailed reflection procedures.
credentialsAndCertsSecrets:
name: confluent-secrets
secureEnv:
sasl.jaas.config: sasl_jaas_config
basic.auth.user.info: basic_auth_user_info
sasl.username: sasl_username
sasl.password: sasl_password
The Actions pod will automatically pick these up in the correctly named environment variables when they are named this exact way.
Contribution
Accepting contributions for a setup script compatible with Confluent Cloud!
The kafka-setup-job container we ship with is only compatible with a distribution of Kafka wherein ZooKeeper is exposed and available. A version of the job using the Confluent CLI would be very useful for the broader community.
